What is syphilis?
What is congenital syphilis?
What is the spread of syphilis?
When do symptoms appear after infection?
Who are at risk for syphilis?
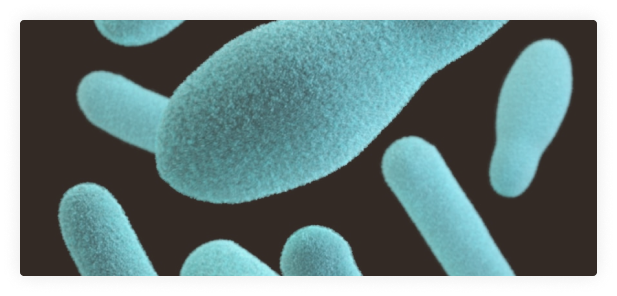
What is Treponema palladium?
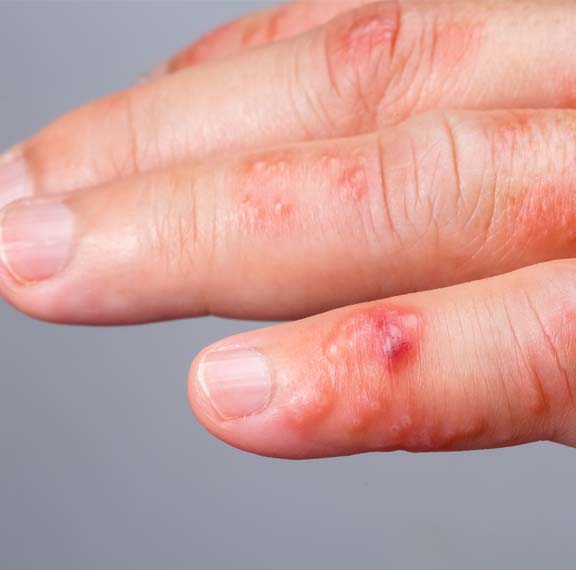
How do syphilis rash look like?
What is the appearance of syphilis chancre?
What is VDRL test?
What is RPR test?
Is syphilis cured?
Is there any chance for reinfection even after being treated?
What is the treatment for syphilis?


.jpg)