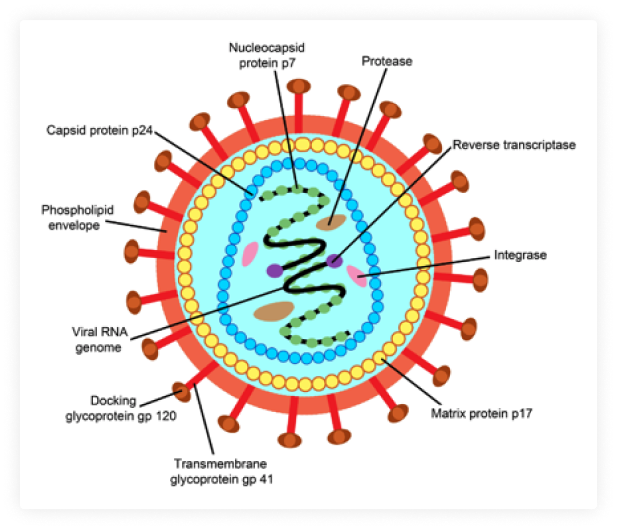
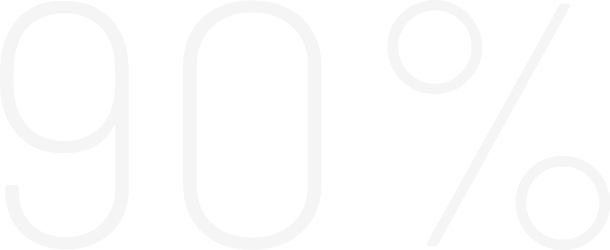HIV/AIDS Trends in Philippines
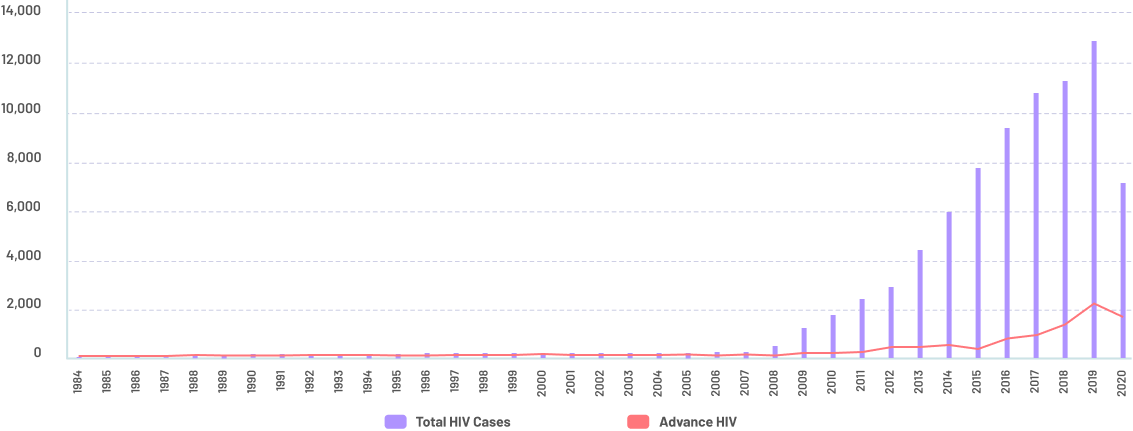
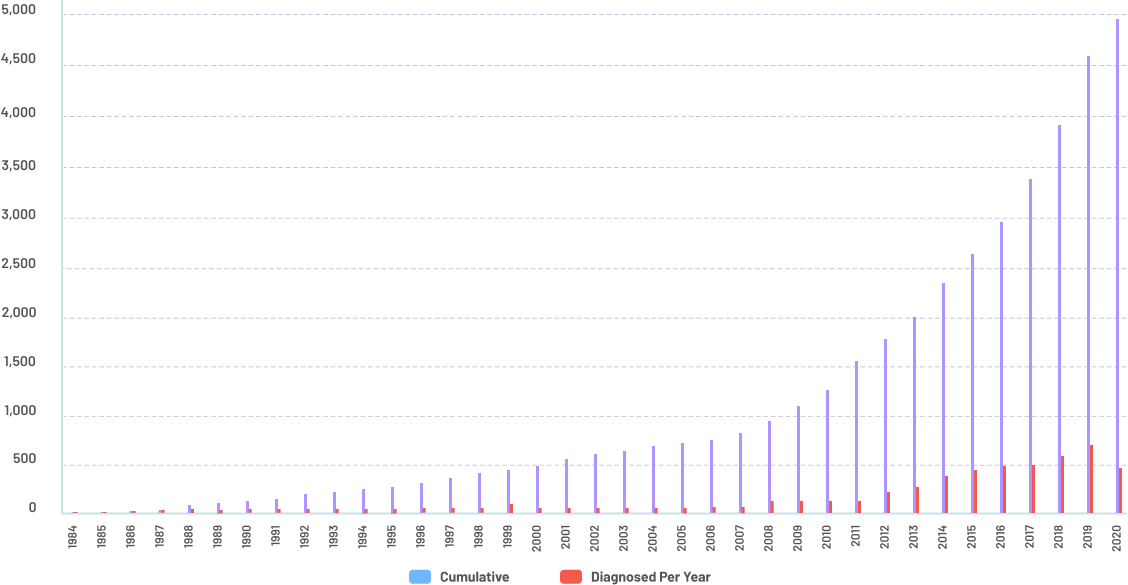
Number of HIV cases and advanced infections reported from Jan 1984 - Nov 2020
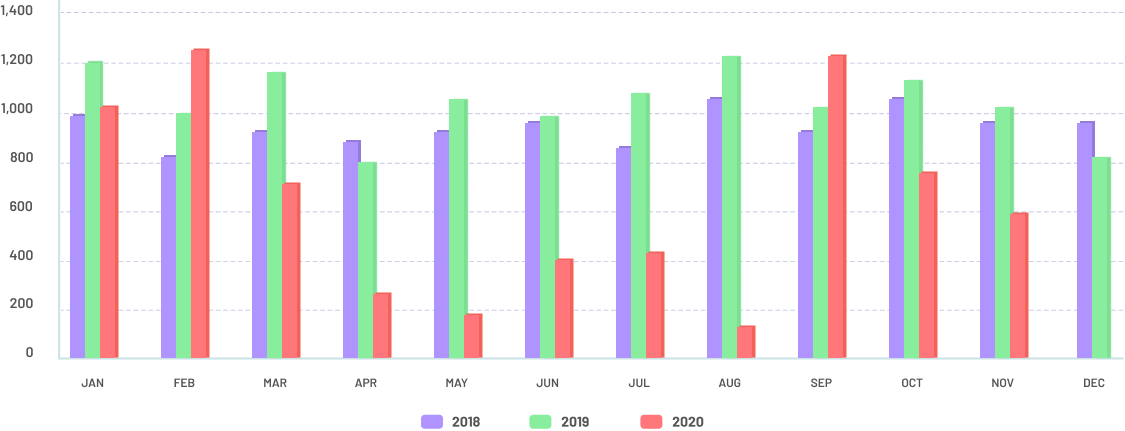
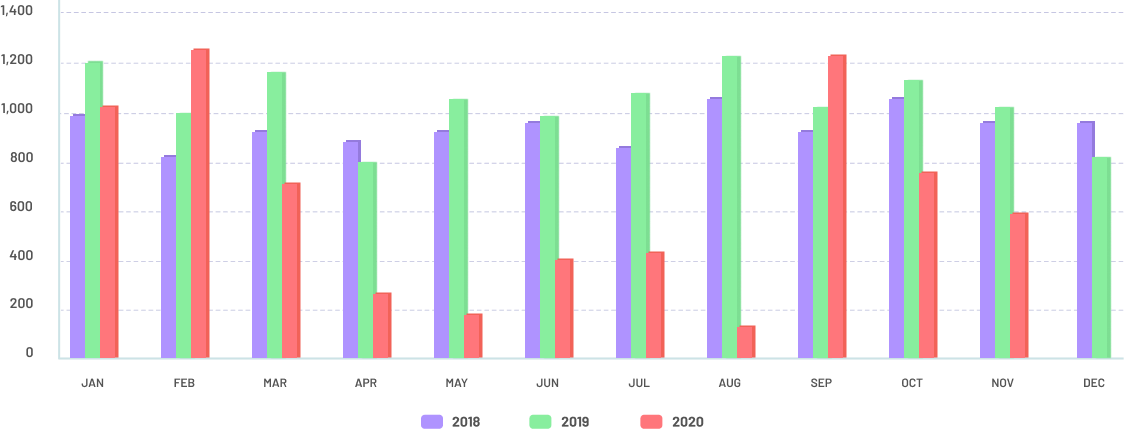
Number of newly diagnosed cases in Philippines
Nearly, there were 620 confirmed HIV-positive individuals reported to the HIV/AIDS & ART Registry of the Philippines (HARP) in November 2020
Number of newly diagnosed cases per month, 2018-2020
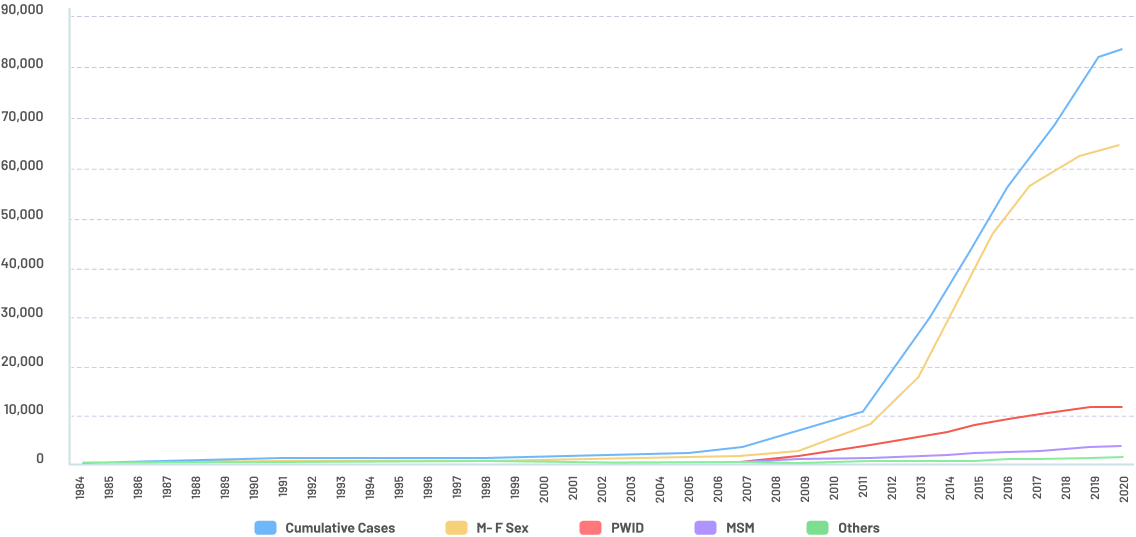
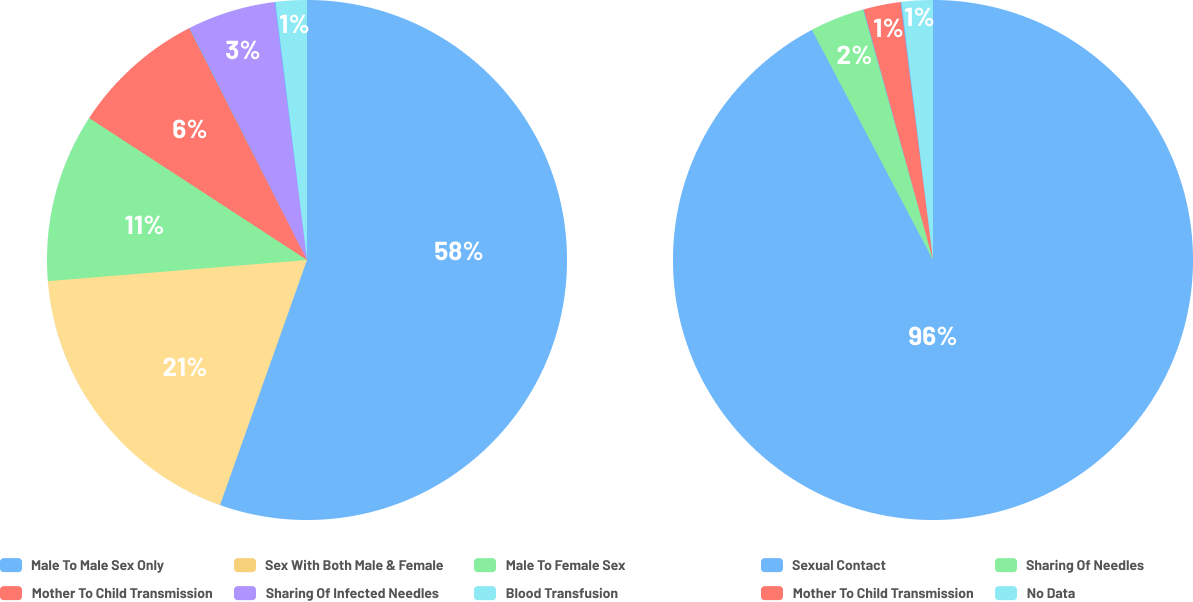
Mode of transmission in Philippines
The primary mode of transmission in Philippines is predominant among:
- Males who have sex with males [MSM] - 86%
- Sexual contact among male –female – 10%
- From 1984 to 2006, the predominant MOT was male-female sex and in 2007 HIV cases were reported among MSM
- The transmission through sharing of infected needles was less than one percent from 1984 – 2004
- Cases among people who inject drugs (PWID) increased in 2010
Cumulative number of people diagnosed per year by MOT, Jan 1984 – Nov 2020
Mode of transmission in Philippines
- Mode of transmission among children and adolescents, Jan 1984 – Nov 2020
- Mode of transmission in youth 15 -24 years old, Jan 1984 – Nov 2020
Females diagnosed with HIV in Philippines
- The number of females diagnosed with HIV from past ten years (2011 -2020) has been increasing
- Data shows that From January to November 2020, 375 females were diagnosed with HIV, which was three times higher compared with cases reported in 2011 (139)
- All female cases which were reported since 1984 were in the reproductive age group (15-49 years old) at the time of testing
Number of females diagnosed per year, Jan 1984 - Nov 2020
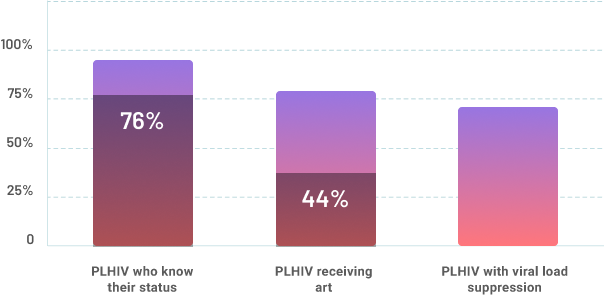
Number of newly diagnosed cases in Philippines
In November 2020, there were 563 people with HIV who were initiated on anti-retroviral therapy
Number of art initiation per month 2018- 2020